Tropical Grassland Biome Food Chain Biology Diagrams The following is an example of a food chain in the grasslands: Producer: Grass; grasslands are tracts of land predominantly covered with different grass species. A food chain is the path In a grassland food chain, the grass is the producer. It produces food using the sun's energy. The primary consumers follow the producers. Insects like grasshoppers are primary grasslands consumers as they depend on the green plant for their food (herbivores). Occasionally, primary consumers are omnivores as well, such as aardvarks. The frog (carnivores) eats the insects, the secondary
The grassland food chain is a dynamic and intricate system that underpins the ecological balance of this vast ecosystem. From the primary producers that capture the sun's energy to the apex predators that regulate populations, each organism plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate equilibrium of life. Understanding the intricacies of

Unveiling the Intricacies of Grassland Food Chains: Energy Transfer ... Biology Diagrams
Grassland food chains encompass intricate webs of energy transfer, with primary producers (grasses, forbs) forming the base and herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers occupying higher trophic levels. Energy flows through the chain, dissipating at each level, while nutrients are cycled through the actions of decomposers. The balance of these food chains is crucial for ecosystem stability, as
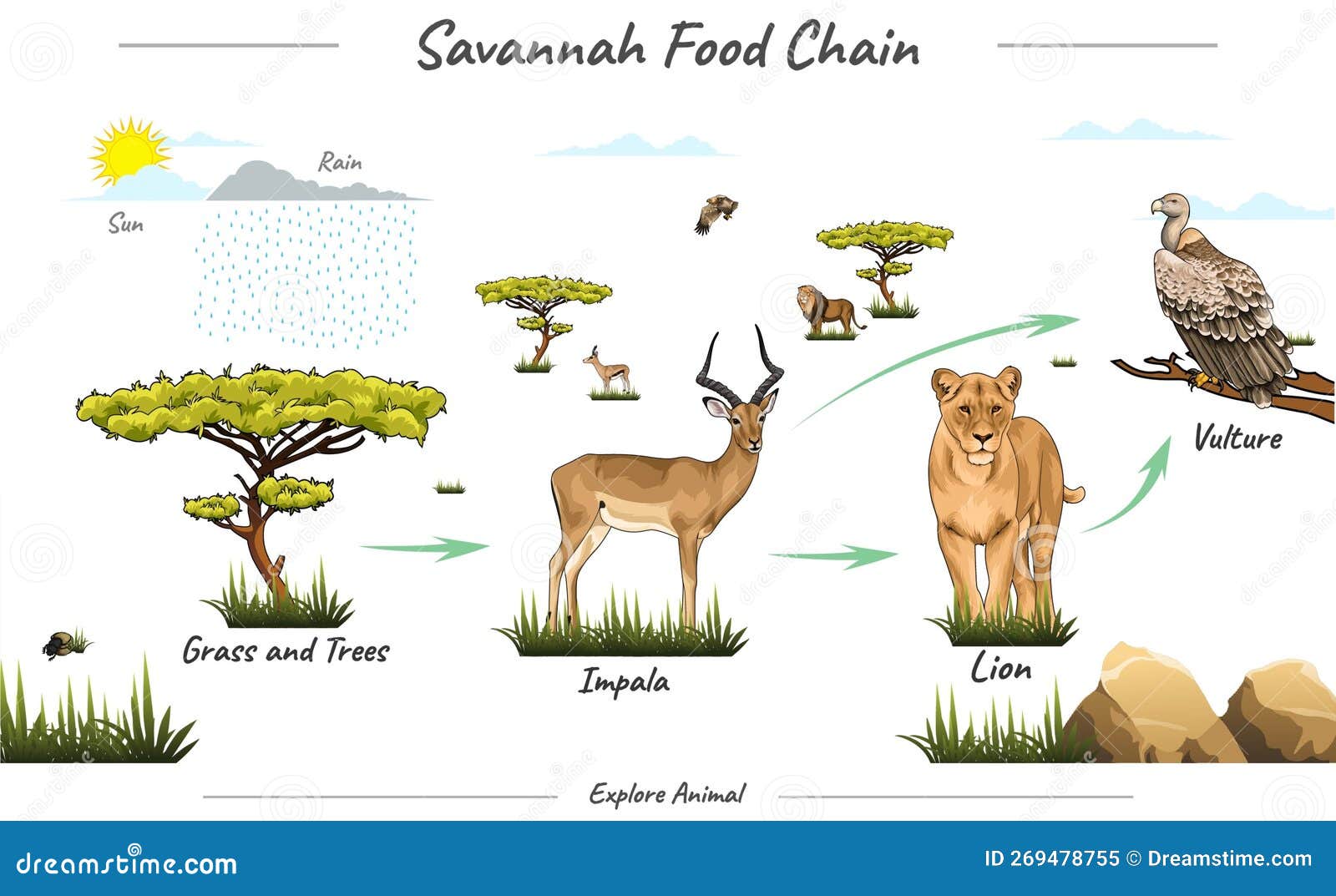
The grass, deer and tiger form a food chain (Figure 8.2). In this food chain, energy flows from the grass (producer) to the deer (primary consumer) to the tiger (secondary consumer). A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants, grasshoppers, frogs, snakes and hawks (Figure 8.3).
Grasslands in the World, Map, Types and Food Chain in Grassland Biology Diagrams
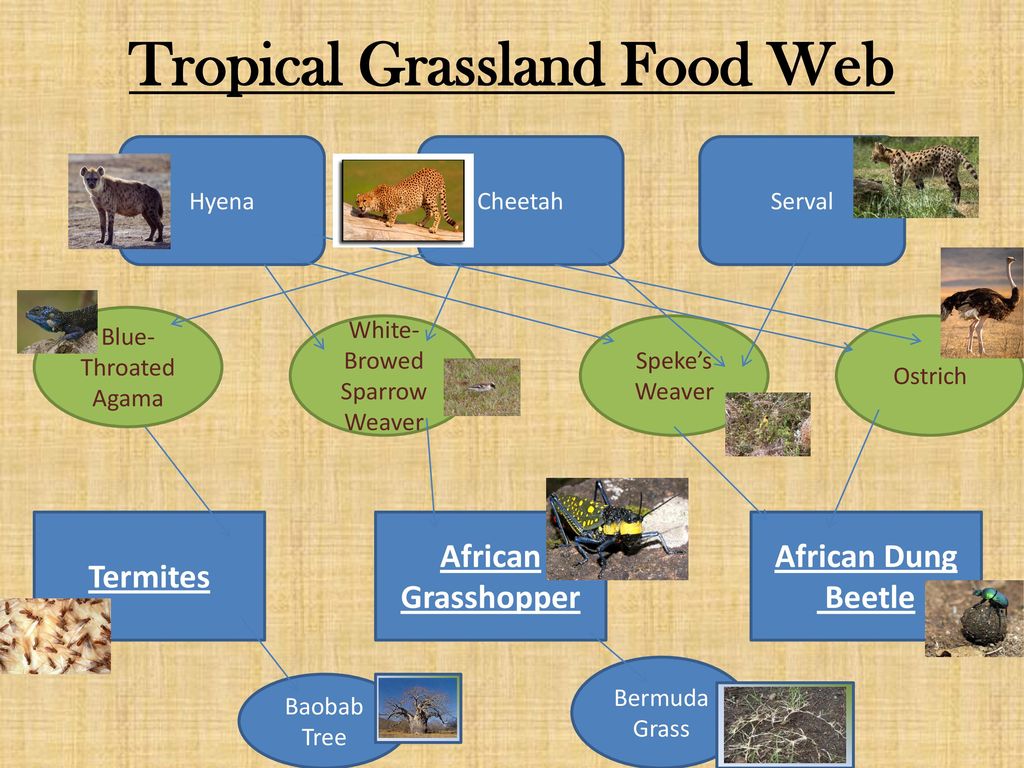
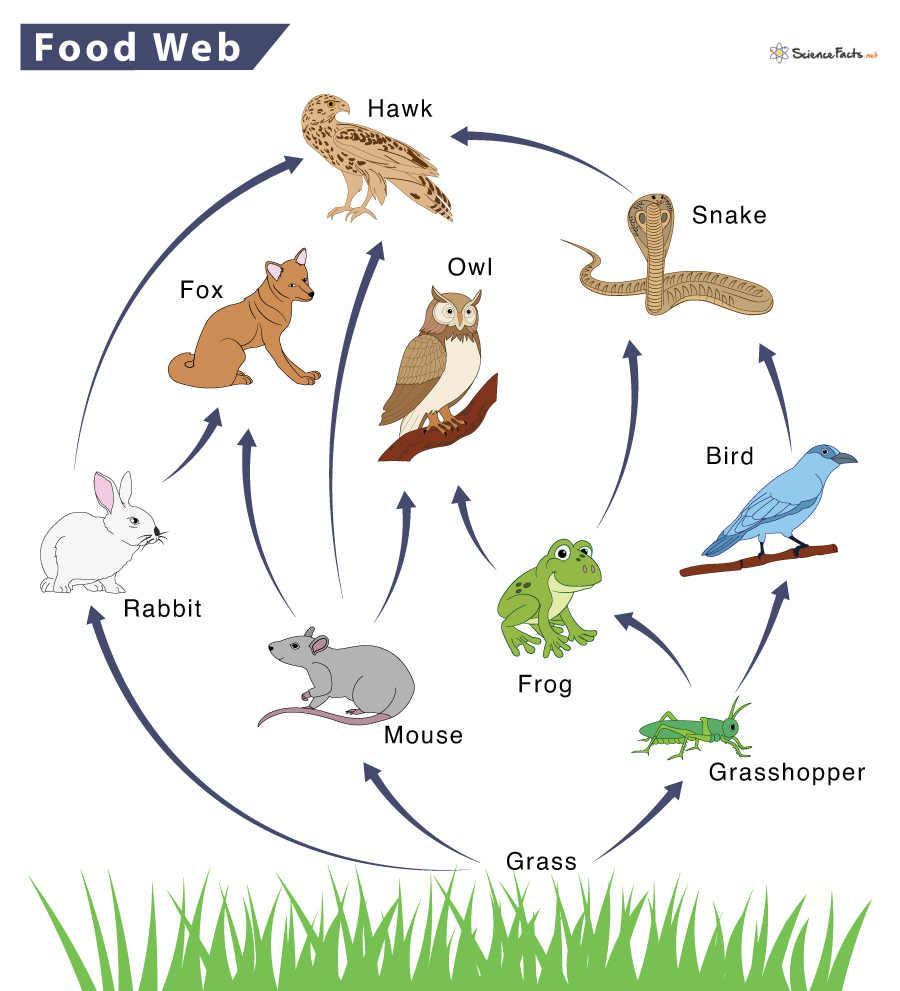
In a grassland food chain, the grass is the producer. It produces food using the sun's energy. The primary consumers follow the producers. Insects like grasshoppers are primary grasslands consumers as they depend on the green plant for their food (herbivores). Occasionally, primary consumers are omnivores as well, such as aardvarks. A grassland food web is a complex network of interrelated food chains that illustrates the feeding relationships between different organisms in a grassland ecosystem. It showcases how energy and nutrients flow through the ecosystem, starting from producers (plants) to various levels of consumers (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores) and decomposers.
