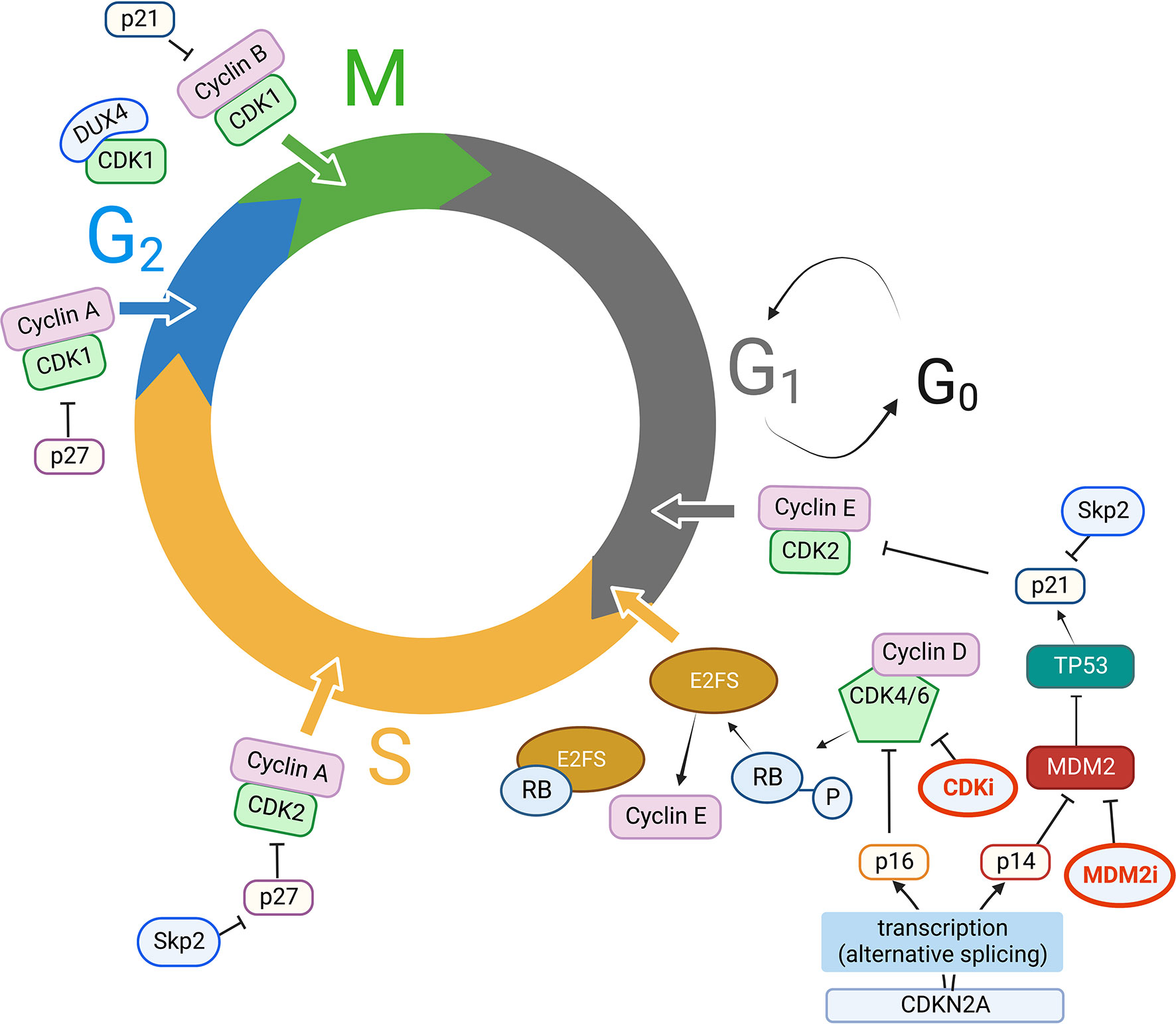
Study Guide Answers Biology Quarter 2 Exam Biology Diagrams This division is useful when talking about most cell cycles, but it is not universal as some cyclins have different functions or timing in different cell types. Protein cyclin A governs this process by keeping the process going until the errors are eliminated. In normal cells, persistent cyclin A expression prevents the stabilization of

Thus, the cyclin and cdk are the proteins that are responsible for guiding cells from one phase of the cell cycle to the next. Cyclins: Types and Regulation in Cell Cycle Control. Cyclins are proteins which binds to enzymes called cyclin dependent kinases (CKD). Many types of cyclins exist which bind to different types of CKDs.
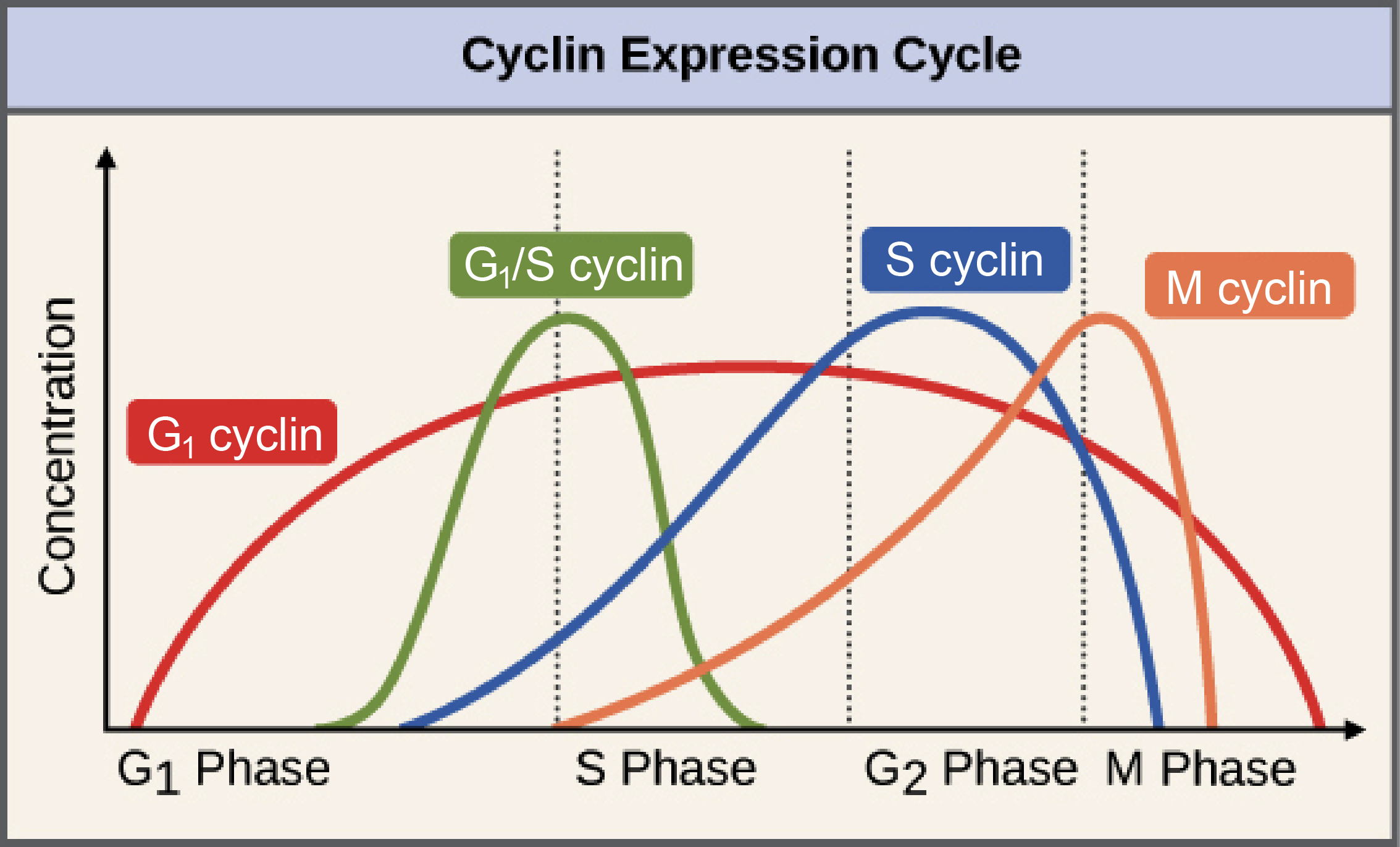
Function of cyclins in regulating the mitotic and meiotic cell cycles ... Biology Diagrams
In mice, cyclin A1 is expressed specifically in testis in pachytene and diplotene spermatocytes spermatocytes in stage IX to XII tubules at both the mRNA and protein levels. 14,18 In contrast, cyclin A2 is expressed in spermatogonia and pre-leptotene spermatocytes and its expression is downregulated early in meiotic prophase, well before cyclin The TFIIH complex, which is a component of a 10-subunit general transcription factor, consists of the regulatory subunit cyclin H, the catalytic subunit CDK7, and a ring finger protein menage a trois 1 (Mat1), which functions as the helicase, ATPase, and protein kinase; it is also the last to be recruited.

Cyclins are a group of stress-sensitive proteins in controlling cell death and survival in DNA damage response. The B-type cyclin, i.e., cyclin B1, is an essential cell cycle component in the regulation of transition from G2 to M phase [127-130].Cyclin B1 and the phosphorylated Cdc2 form a complex with 14-3-3 proteins [131] that accelerates cyclin B1/Cdc2 translocation into the nucleus to Next, CDK2/cyclin E function is inhibited and on G 1 cyclin-dependent kinases inhibition, proteins that belong to the retinoblastoma protein family are turned back to their hypophosphorylated active state and cells exit the cycle . Figure 3.

Cyclin - an overview Biology Diagrams
Another example of a target protein is the phosphorylation of p27, which usually functions to inhibit Rb. Phosphorylation by CDK-2-cyclin E complex prevents this inhibition and so progression from